The Life-Saving Power of CPR: Essential Medical Terms You Should Know
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a critical skill that can mean the difference between life and death during a cardiac emergency. At Pulse CPR and First Aid School, we train individuals and healthcare professionals to deliver high-quality CPR, ensuring the best chance of survival for victims of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and other life-threatening conditions. In this post, we’ll explore 50 essential CPR-related medical terms that every rescuer should know.
Understanding the Basics of CPR
CPR is designed to restore circulation and oxygenation when the heart stops beating due to cardiac arrest. Effective chest compressions and rescue breaths help maintain blood flow to the myocardium and brain, increasing the likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
- Airway – The passage for air entering and exiting the lungs.
- Apnea – A temporary cessation of breathing.
- Asphyxia – A condition arising when the body is deprived of oxygen.
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED) – A portable device that delivers a shock to correct fibrillation.
- Bag-Valve Mask (BVM) – A device used to assist ventilation.
- Brachial Pulse – A pulse found in the arm, used for infants.
- Bradycardia – A slower-than-normal heart rate.
- Cardiac Arrest – The sudden stopping of the heart.
- Carotid Pulse – A pulse felt along the carotid artery in the neck.
- Chest Compressions – Rhythmic pressing on the sternum to maintain circulation.
The Role of Oxygen and Ventilation in CPR
Ensuring adequate ventilation is crucial during CPR. A lack of oxygen can lead to hypoxia, causing further damage to vital organs.
- Circulation – The movement of blood throughout the body.
- Compression Depth – The proper depth for chest compressions.
- Compression Rate – The speed of compressions per minute.
- Coronary Arteries – Blood vessels that supply the heart muscle.
- Defibrillation – The process of delivering an electric shock to restore heart rhythm.
- Diastolic Pressure – The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest.
- Dyspnea – Shortness of breath.
- Emergency Medical Services (EMS) – The system providing emergency care.
- Epiglottis – A flap of tissue preventing food from entering the airway.
- Fibrillation – Rapid and irregular heart contractions.
Recognizing and Responding to an Emergency
Knowing how to respond to a foreign body airway obstruction (FBAO) or obstructed airway is vital.
- Foreign Body Airway Obstruction (FBAO) – A blockage in the airway.
- Glottis – The part of the larynx that opens and closes for airflow.
- Gasping Respirations – Abnormal breathing indicating cardiac distress.
- Hands-Only CPR – CPR technique using only chest compressions.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) – A blockage in the coronary arteries.
- Hemodynamics – The study of blood flow.
- Hypoxia – A deficiency of oxygen in the body.
- Larynx – The voice box, important in breathing.
- Life Support – Medical interventions to maintain life.
- Myocardium – The heart muscle.
Tools and Techniques for Effective CPR
Using proper oxygen saturation (SpO2) monitoring can help gauge oxygen levels in a patient.
- Nasal Cannula – A device for delivering oxygen.
- Obstructed Airway – A blockage preventing breathing.
- Oropharyngeal Airway (OPA) – A device that keeps the airway open.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) – The level of oxygen in the blood.
- Palpation – The process of feeling for a pulse check.
- Perfusion – The passage of fluid through the circulatory system.
- Precordial Thump – A technique used in emergencies to restart the heart.
- Pulmonary Arrest – The stopping of lung function.
- Pulmonary Edema – Fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Pulse Check – Checking for a pulse to assess heart activity.
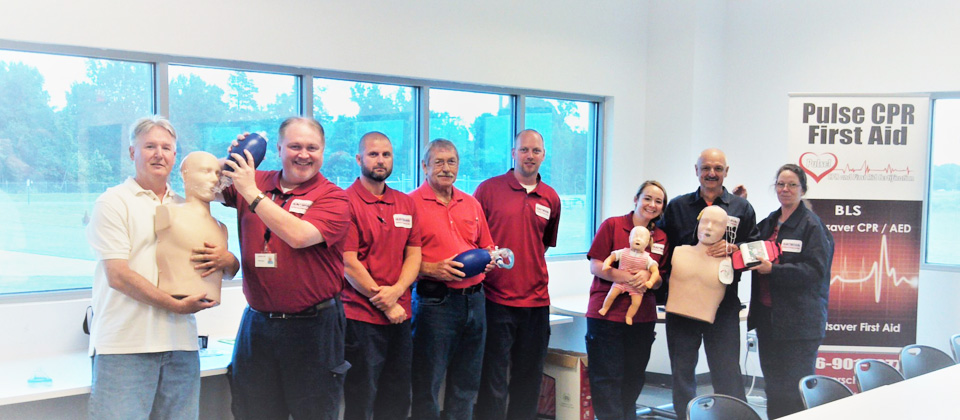
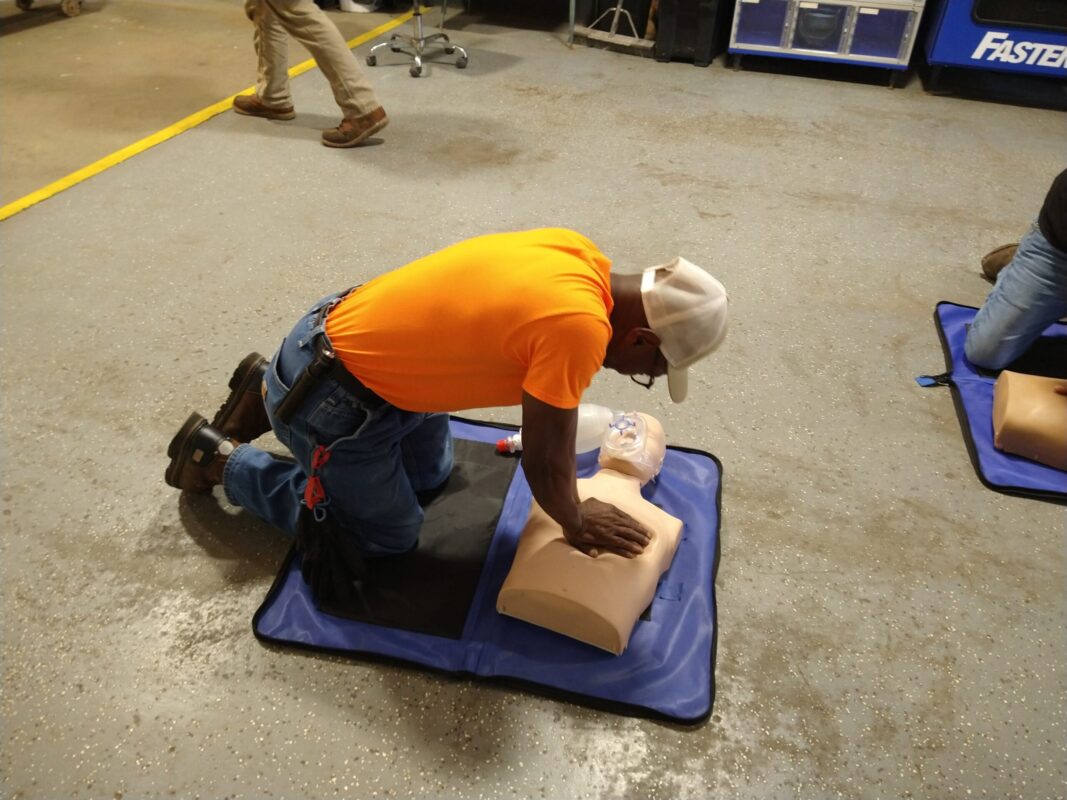


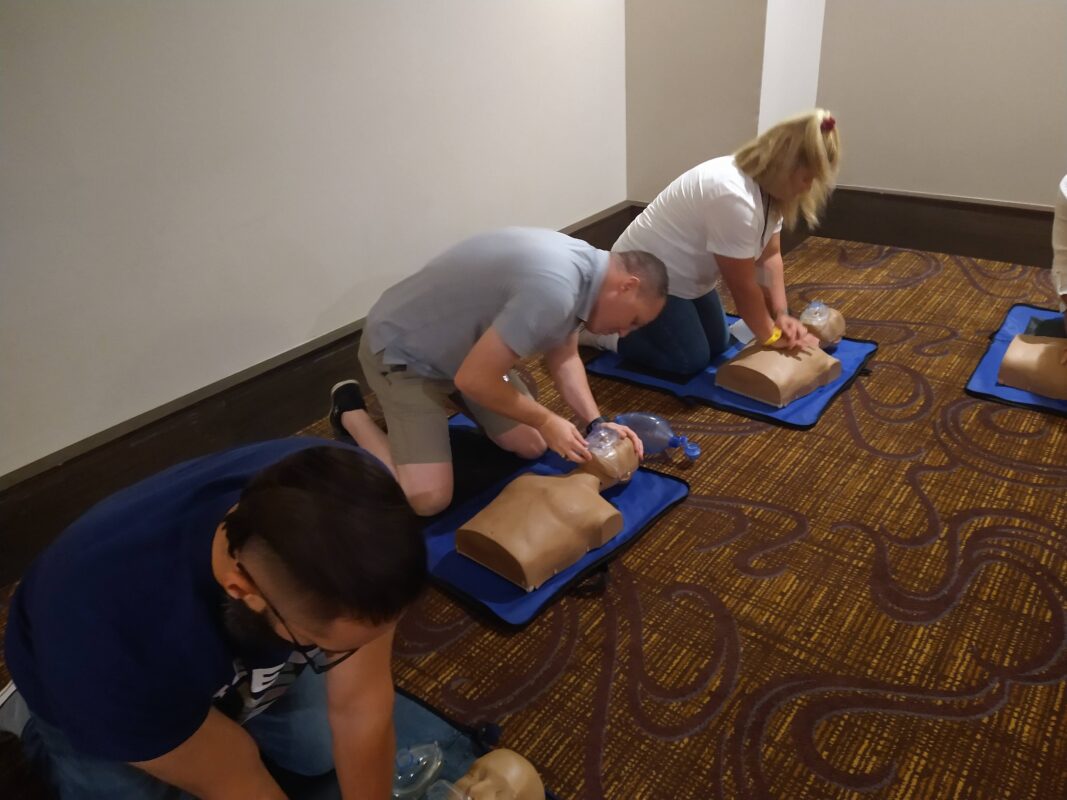




CPR Training and Certification
At Pulse CPR and First Aid School, we emphasize proper technique and practice, ensuring that rescuers are prepared for real-life emergencies.
- Rescue Breaths – Artificial breaths given during CPR.
- Respiratory Arrest – A cessation of breathing.
- Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) – The return of a heartbeat after CPR.
- Shockable Rhythm – Heart rhythms that can be corrected with defibrillation.
- Sternum – The breastbone where chest compressions are performed.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) – A sudden loss of heart function.
- Systolic Pressure – The pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
- Ventilation – The process of moving air in and out of the lungs.
Be Prepared, Save Lives
CPR saves lives, and being trained can help you make a difference in an emergency. Whether you are a healthcare provider, teacher, or concerned citizen, CPR training at Pulse CPR and First Aid School equips you with the skills and confidence to act when needed most.
Contact us today to sign up for a class and become CPR-certified. Be the difference when seconds count!

